Multi-AZ vs. Multi-Region
When's the right time to go Multi region compared to Multi AZ?
Early this year, AWS officially unveiled its newest Australia region in Melbourne. This has caused many a conversation amongst customers as to whether now is the right time to look into a multi-region strategy or if a multiple availability zone strategy is the most cost-effective way of having an adequate disaster recovery plan.
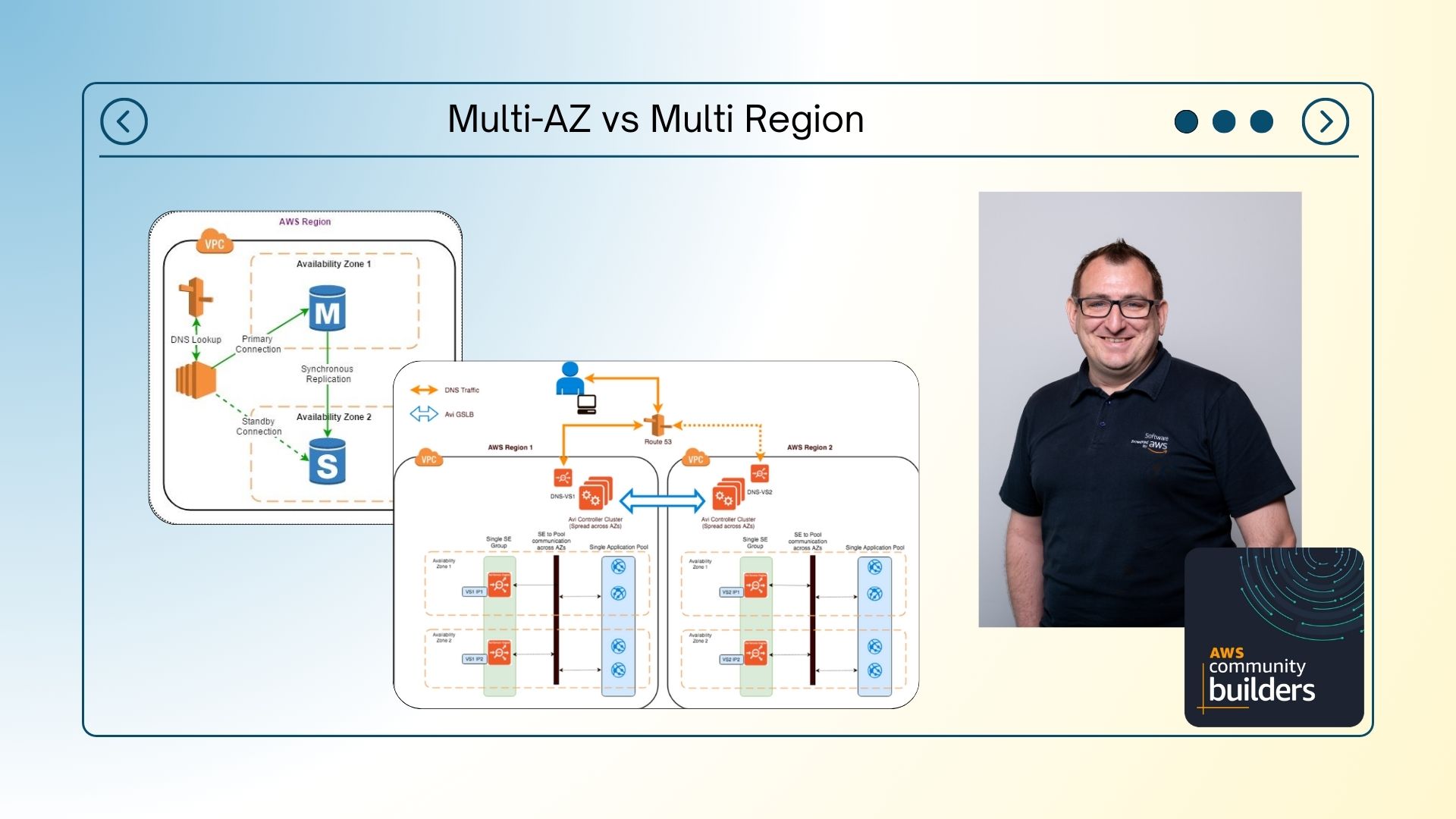
What is an “AZ” and a “Region”?
Before we start, let us just define a Region and an Availability Zone (AZ);
“An Availability Zone (AZ) is one or more discrete data centers with redundant power, networking, and connectivity in an AWS Region. AZs give customers the ability to operate production applications and databases that are more highly available, fault tolerant, and scalable than would be possible from a single data center. All AZs in an AWS Region are interconnected with high-bandwidth, low-latency networking, over fully redundant, dedicated metro fiber providing high-throughput, low-latency networking between AZs. All traffic between AZs is encrypted. The network performance is sufficient to accomplish synchronous replication between AZs. AZs make partitioning applications for high availability easy. If an application is partitioned across AZs, companies are better isolated and protected from issues such as power outages, lightning strikes, tornadoes, earthquakes, and more. AZs are physically separated by a meaningful distance, many kilometers, from any other AZ, although all are within 100 km (60 miles) of each other.”
“AWS has the concept of a Region, which is a physical location around the world where we cluster data centers. We call each group of logical data centers an Availability Zone. Each AWS Region consists of a minimum of three, isolated, and physically separate AZs within a geographic area. Unlike other cloud providers, who often define a region as a single data center, the multiple AZ design of every AWS Region offers advantages for customers. Each AZ has independent power, cooling, and physical security and is connected via redundant, ultra-low-latency networks. AWS customers focused on high availability can design their applications to run in multiple AZs to achieve even greater fault-tolerance. AWS infrastructure Regions meet the highest levels of security, compliance, and data protection.”
Source: https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/global-infrastructure/regions_az/
Comparing Multiple Availability Zone (Multi-AZ) deployments with Multiple Region deployments in AWS is a crucial topic when designing a resilient and highly available infrastructure. Let’s explore the benefits and potential drawbacks of each approach.
Multiple Availability Zone (Multi-AZ) Deployments
Benefits
- High Availability - Multi-AZ deployments replicate your resources across multiple Availability Zones within a single AWS region This provides high availability and fault tolerance. If one Availability Zone experiences an outage, traffic can be redirected to another with minimal disruption (1 - 2 mins).
- Low Latency - Since all resources are within the same region, the latency between resources is generally lower compared to a Multi-Region setup.
- Simplified Management - Managing resources within a single region can be simpler and less complex compared to dealing with multiple regions.
- Cost-Efficiency - Running resources in a single region can often be more cost-effective than replicating resources across multiple regions.
Drawbacks
- Limited Disaster Recovery - While Multi-AZ deployments offer excellent availability, they are still susceptible to regional-level failures, such as a widespread power outage or a natural disaster affecting an entire region.
- Compliance Requirements - If specific compliance regulations require geographic separation of data, Multi-AZ might not be sufficient.
Multiple-Region Deployments
Benefits
- Disaster Recovery - Multi-Region deployments provide stronger disaster recovery capabilities. If a complete region goes down, resources in another region can take over, ensuring business continuity.
- Compliance and Data Residency - For regulatory reasons, you might need to store data in specific geographic regions. Multi-Region deployments can help meet these requirements.
- Reduced Risk - By distributing resources across geographically distinct locations, you reduce the risk of a single event affecting all your resources.
Drawbacks
- Higher Latency - Traffic between regions generally has higher latency compared to within a single region.
- Complexity - Managing resources across multiple regions increases complexity, as you need to ensure data synchronization, application consistency, and potentially adapt to different regional limitations.
- Higher Costs - Running resources in multiple regions can increase costs due to data transfer fees, higher redundancy requirements, and the need for more complex architecture.
What’s the cost of “High availability?”
One of the common relationships, or trade-offs, between Multi-Az and Multi-Region is the cost of High availability (HA). High availability is regularly referred to as a number of 9’s. The more 9’s, the less downtime. E.g.
| Availability | Downtime per year (Hours) |
|---|---|
| 90 % (“one nine”) | 876.72 |
| 95% (“one nine five”) | 438.24 |
| 97% (“one nine seven”) | 263.04 |
| 98% (“one nine eight”) | 175.44 |
| 99% (“two nines”) | 87.6 |
| 99.5% (“two nines five”) | 43.92 |
| 99.8% (“two nines eight”) | 17.53 |
| 99.9% (“three nines”) | 8.77 |
| 99.95% (“three nines five”) | 4.38 |
| 99.99% (“four nines”) | 0.8766666667 |
However in chasing these reduced downtimes and more 9’s of HA, the cost of doing so increases exponentially, causing diminishing returns / lower ROI / “less bang for buck”. This can be illustrated as such;
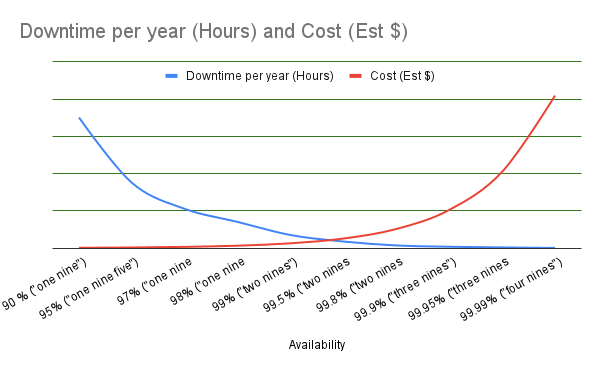
The chart above illustrates a generalised hypothesis that once you start evaluating your requirements for HA requirements vs Cost you’ll regularly find a sweet spot.
Most Startups and SMB’s are quite happy with settling on 99.5% or lower in order to keep costs manageable.
Conclusion
In summary, choosing between Multi-AZ and Multi-Region deployments depends on your specific needs, risk tolerance, and budget considerations. For critical applications, a Multi-Region approach provides superior disaster recovery capabilities but comes with higher complexity and costs. Multi-AZ deployments are simpler to manage, cost-effective, and provide excellent availability within a single region.
It’s also worth noting that AWS offers services like Amazon Route 53 for global traffic management and Amazon S3 cross-region replication to enhance the resilience and availability of your applications regardless of the chosen deployment strategy.
